ملاحظة
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
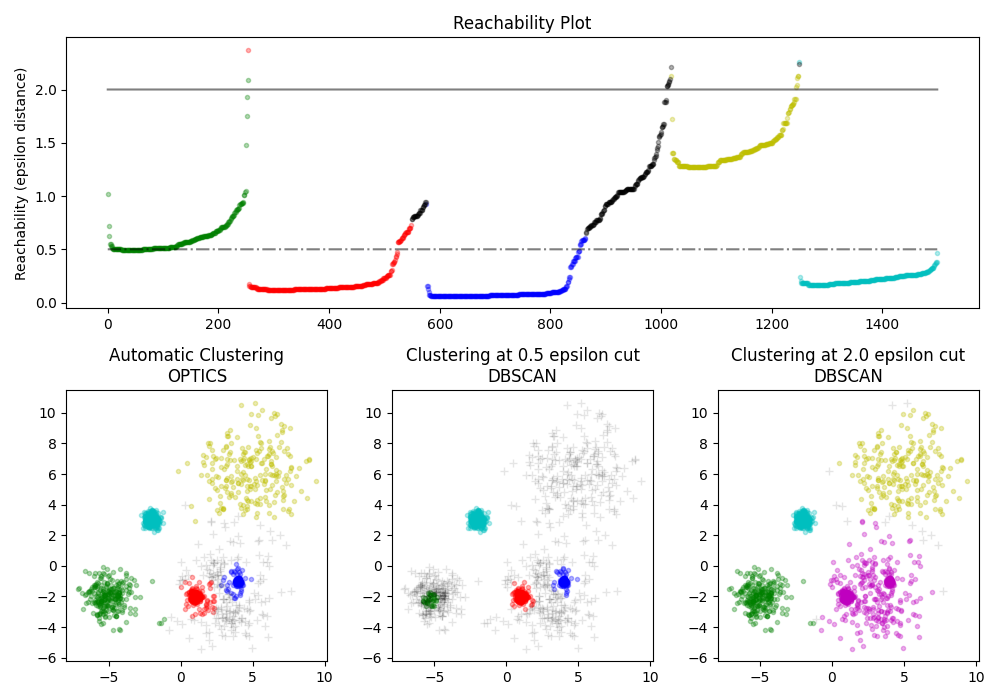
عرض توضيحي لخوارزمية التجميع OPTICS#
يحدد العينات الأساسية ذات الكثافة العالية ويوسع التجمعات منها. يستخدم هذا المثال بيانات تم إنشاؤها بحيث يكون للتجمعات كثافات مختلفة.
يتم استخدام OPTICS أولاً مع طريقة اكتشاف التجمعات Xi الخاصة به، ثم تعيين عتبات محددة على إمكانية الوصول، والتي
تتوافق مع DBSCAN. يمكننا أن نرى أن التجمعات المختلفة
لطريقة Xi في OPTICS يمكن استردادها مع خيارات مختلفة
العتبات في DBSCAN.
# المؤلفون: مطوري scikit-learn
# تعريف الترخيص: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import OPTICS, cluster_optics_dbscan
# توليد بيانات العينة
np.random.seed(0)
n_points_per_cluster = 250
C1 = [-5, -2] + 0.8 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2)
C2 = [4, -1] + 0.1 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2)
C3 = [1, -2] + 0.2 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2)
C4 = [-2, 3] + 0.3 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2)
C5 = [3, -2] + 1.6 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2)
C6 = [5, 6] + 2 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2)
X = np.vstack((C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6))
clust = OPTICS(min_samples=50, xi=0.05, min_cluster_size=0.05)
# Run the fit
clust.fit(X)
labels_050 = cluster_optics_dbscan(
reachability=clust.reachability_,
core_distances=clust.core_distances_,
ordering=clust.ordering_,
eps=0.5,
)
labels_200 = cluster_optics_dbscan(
reachability=clust.reachability_,
core_distances=clust.core_distances_,
ordering=clust.ordering_,
eps=2,
)
space = np.arange(len(X))
reachability = clust.reachability_[clust.ordering_]
labels = clust.labels_[clust.ordering_]
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
G = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 3)
ax1 = plt.subplot(G[0, :])
ax2 = plt.subplot(G[1, 0])
ax3 = plt.subplot(G[1, 1])
ax4 = plt.subplot(G[1, 2])
# Reachability plot
colors = ["g.", "r.", "b.", "y.", "c."]
for klass, color in enumerate(colors):
Xk = space[labels == klass]
Rk = reachability[labels == klass]
ax1.plot(Xk, Rk, color, alpha=0.3)
ax1.plot(space[labels == -1], reachability[labels == -1], "k.", alpha=0.3)
ax1.plot(space, np.full_like(space, 2.0, dtype=float), "k-", alpha=0.5)
ax1.plot(space, np.full_like(space, 0.5, dtype=float), "k-.", alpha=0.5)
ax1.set_ylabel("Reachability (epsilon distance)")
ax1.set_title("Reachability Plot")
# OPTICS
colors = ["g.", "r.", "b.", "y.", "c."]
for klass, color in enumerate(colors):
Xk = X[clust.labels_ == klass]
ax2.plot(Xk[:, 0], Xk[:, 1], color, alpha=0.3)
ax2.plot(X[clust.labels_ == -1, 0], X[clust.labels_ == -1, 1], "k+", alpha=0.1)
ax2.set_title("Automatic Clustering\nOPTICS")
# DBSCAN at 0.5
colors = ["g.", "r.", "b.", "c."]
for klass, color in enumerate(colors):
Xk = X[labels_050 == klass]
ax3.plot(Xk[:, 0], Xk[:, 1], color, alpha=0.3)
ax3.plot(X[labels_050 == -1, 0], X[labels_050 == -1, 1], "k+", alpha=0.1)
ax3.set_title("Clustering at 0.5 epsilon cut\nDBSCAN")
# DBSCAN at 2.
colors = ["g.", "m.", "y.", "c."]
for klass, color in enumerate(colors):
Xk = X[labels_200 == klass]
ax4.plot(Xk[:, 0], Xk[:, 1], color, alpha=0.3)
ax4.plot(X[labels_200 == -1, 0], X[labels_200 == -1, 1], "k+", alpha=0.1)
ax4.set_title("Clustering at 2.0 epsilon cut\nDBSCAN")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.803 seconds)
Related examples
تحليل نوع أولوية التركيز لخوارزمية التباين بايزي غاوسي ميكسشر
تحليل نوع أولوية التركيز لخوارزمية التباين بايزي غاوسي ميكسشر