ملاحظة
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
الموازنة بين تعقيد النموذج ودرجة الدقة عبر التحقق المتقاطع#
هذا المثال يوازن بين تعقيد النموذج ودرجة الدقة عبر التحقق المتقاطع من خلال تحقيق دقة جيدة ضمن انحراف معياري واحد لأفضل درجة دقة مع تقليل عدد مكونات PCA [1].
يوضح الشكل التوازن بين درجة الدقة عبر التحقق المتقاطع وعدد مكونات PCA. وتكون الحالة المتوازنة عندما يكون n_components=10 وaccuracy=0.88، والتي تقع ضمن نطاق انحراف معياري واحد لأفضل درجة دقة.
[1] هاستي، ت.، تيبشيران، ر.، فريدمان، ج. (2001). تقييم واختيار النماذج. عناصر التعلم الإحصائي (الصفحات 219-260). نيويورك، نيويورك، الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية: سبرينجر نيويورك.
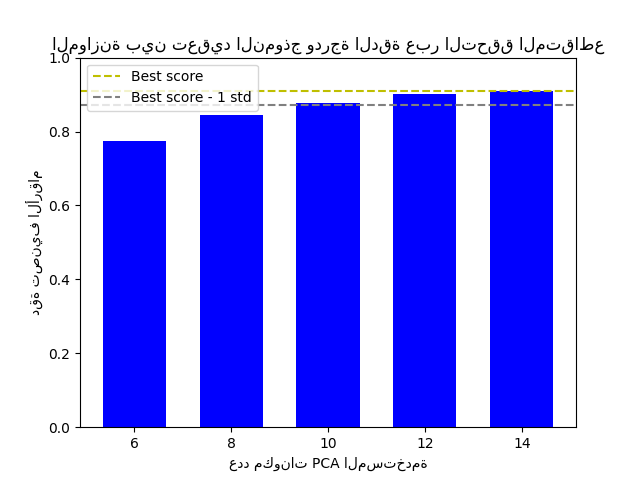
The best_index_ is 2
The n_components selected is 10
The corresponding accuracy score is 0.88
# المؤلفون: مطوري سكايت-ليرن
# معرف الترخيص: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
def lower_bound(cv_results):
"""
حساب الحد الأدنى ضمن انحراف معياري واحد
لأفضل `mean_test_scores`.
المعاملات
----------
cv_results : dict of numpy(masked) ndarrays
راجع cv_results_ الخاص بـ `GridSearchCV`
العائدات
-------
float
الحد الأدنى ضمن انحراف معياري واحد لأفضل
`mean_test_score`.
"""
best_score_idx = np.argmax(cv_results["mean_test_score"])
return (
cv_results["mean_test_score"][best_score_idx]
- cv_results["std_test_score"][best_score_idx]
)
def best_low_complexity(cv_results):
"""
الموازنة بين تعقيد النموذج ودرجة الدقة عبر التحقق المتقاطع.
المعاملات
----------
cv_results : dict of numpy(masked) ndarrays
راجع cv_results_ الخاص بـ `GridSearchCV`.
العائدات
------
int
مؤشر نموذج يحتوي على أقل عدد من مكونات PCA
بينما تكون درجة دقته ضمن انحراف معياري واحد لأفضل
`mean_test_score`.
"""
threshold = lower_bound(cv_results)
candidate_idx = np.flatnonzero(cv_results["mean_test_score"] >= threshold)
best_idx = candidate_idx[
cv_results["param_reduce_dim__n_components"][candidate_idx].argmin()
]
return best_idx
pipe = Pipeline(
[
("reduce_dim", PCA(random_state=42)),
("classify", LinearSVC(random_state=42, C=0.01)),
]
)
param_grid = {"reduce_dim__n_components": [6, 8, 10, 12, 14]}
grid = GridSearchCV(
pipe,
cv=10,
n_jobs=1,
param_grid=param_grid,
scoring="accuracy",
refit=best_low_complexity,
)
X, y = load_digits(return_X_y=True)
grid.fit(X, y)
n_components = grid.cv_results_["param_reduce_dim__n_components"]
test_scores = grid.cv_results_["mean_test_score"]
plt.figure()
plt.bar(n_components, test_scores, width=1.3, color="b")
lower = lower_bound(grid.cv_results_)
plt.axhline(np.max(test_scores), linestyle="--", color="y", label="Best score")
plt.axhline(lower, linestyle="--", color=".5", label="Best score - 1 std")
plt.title("الموازنة بين تعقيد النموذج ودرجة الدقة عبر التحقق المتقاطع")
plt.xlabel("عدد مكونات PCA المستخدمة")
plt.ylabel("دقة تصنيف الأرقام")
plt.xticks(n_components.tolist())
plt.ylim((0, 1.0))
plt.legend(loc="upper left")
best_index_ = grid.best_index_
print("The best_index_ is %d" % best_index_)
print("The n_components selected is %d" % n_components[best_index_])
print(
"The corresponding accuracy score is %.2f"
% grid.cv_results_["mean_test_score"][best_index_]
)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.172 seconds)
Related examples
استراتيجية إعادة الضبط المخصصة للبحث الشبكي مع التحقق المتقاطع

مقارنة بين نماذج الغابات العشوائية ورفع التدرج بالرسم البياني