ملاحظة
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
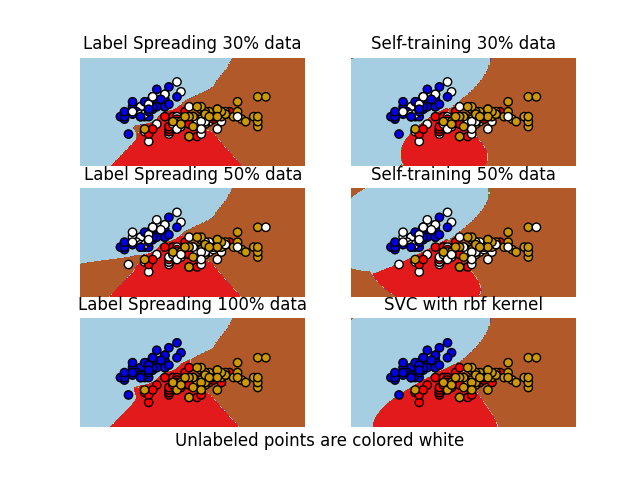
حدود القرار للمصنفات شبه المُشرفة مقابل SVM على مجموعة بيانات Iris#
مقارنة لحدود القرار المولدة على مجموعة بيانات Iris بواسطة Label Spreading وSelf-training وSVM.
هذا المثال يوضح أن Label Spreading وSelf-training يمكنهما تعلم حدود جيدة حتى مع كميات صغيرة من البيانات المُعَلَّمة.
ملاحظة: تم إهمال Self-training مع 100% من البيانات لأنها متطابقة وظيفياً مع تدريب SVC على 100% من البيانات.
# المؤلفون: مطوري scikit-learn
# معرف الترخيص: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.semi_supervised import LabelSpreading, SelfTrainingClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2]
y = iris.target
# حجم الخطوة في الشبكة
h = 0.02
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
y_rand = rng.rand(y.shape[0])
y_30 = np.copy(y)
y_30[y_rand < 0.3] = -1 # تعيين عينات عشوائية لتكون غير مُعَلَّمة
y_50 = np.copy(y)
y_50[y_rand < 0.5] = -1
# ننشئ مثالاً لـ SVM ونقوم بتدريبه على البيانات. لا نقوم بضبط البيانات لأننا نريد رسم المتجهات الداعمة
ls30 = (LabelSpreading().fit(X, y_30), y_30, "Label Spreading 30% data")
ls50 = (LabelSpreading().fit(X, y_50), y_50, "Label Spreading 50% data")
ls100 = (LabelSpreading().fit(X, y), y, "Label Spreading 100% data")
# المصنف الأساسي لـ self-training مطابق لـ SVC
base_classifier = SVC(kernel="rbf", gamma=0.5, probability=True)
st30 = (
SelfTrainingClassifier(base_classifier).fit(X, y_30),
y_30,
"Self-training 30% data",
)
st50 = (
SelfTrainingClassifier(base_classifier).fit(X, y_50),
y_50,
"Self-training 50% data",
)
rbf_svc = (SVC(kernel="rbf", gamma=0.5).fit(X, y), y, "SVC with rbf kernel")
# إنشاء شبكة لرسمها
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
color_map = {-1: (1, 1, 1), 0: (0, 0, 0.9), 1: (1, 0, 0), 2: (0.8, 0.6, 0)}
classifiers = (ls30, st30, ls50, st50, ls100, rbf_svc)
for i, (clf, y_train, title) in enumerate(classifiers):
# رسم حدود القرار. لهذا، سنقوم بتعيين لون لكل نقطة
# في الشبكة [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max].
plt.subplot(3, 2, i + 1)
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
# وضع النتيجة في رسم ملون
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
plt.axis("off")
# رسم نقاط التدريب أيضاً
colors = [color_map[y] for y in y_train]
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=colors, edgecolors="black")
plt.title(title)
plt.suptitle("Unlabeled points are colored white", y=0.1)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.269 seconds)
Related examples
تصنيف العملية الغاوسية (GPC) على مجموعة بيانات iris
تصنيف العملية الغاوسية (GPC) على مجموعة بيانات iris
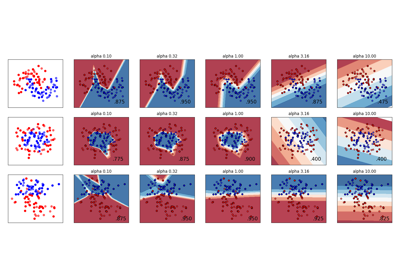
تغيير معامل التنظيم في الشبكة العصبية متعددة الطبقات
تغيير معامل التنظيم في الشبكة العصبية متعددة الطبقات