ملاحظة
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
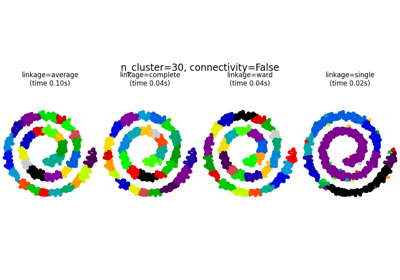
مختلف خوارزميات التجميع الهرمي على تضمين ثنائي الأبعاد لمجموعة بيانات الأرقام#
وثيقة توضيحية لخيارات الربط المختلفة للتجميع الهرمي على تضمين ثنائي الأبعاد لمجموعة بيانات الأرقام.
الهدف من هذا المثال هو إظهار بشكل بديهي كيف تتصرف المقاييس، وليس العثور على أفضل أقسام للأرقام. لهذا السبب يعمل المثال على تضمين ثنائي الأبعاد.
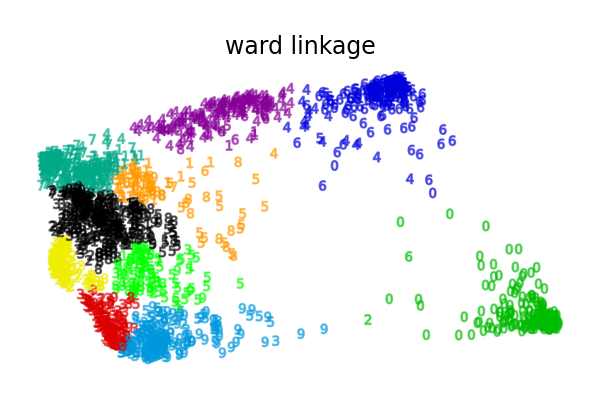
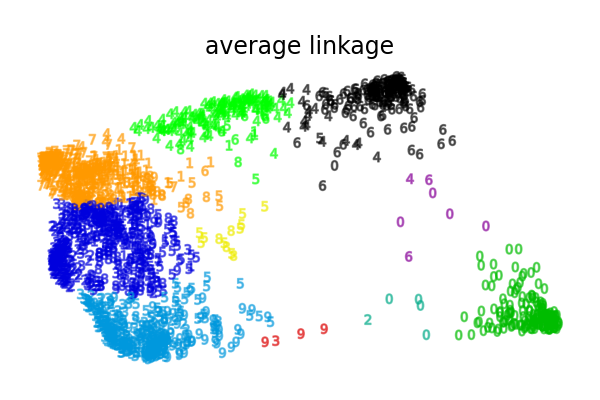
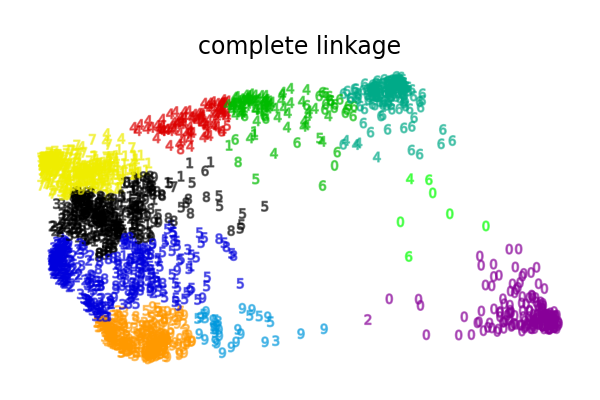
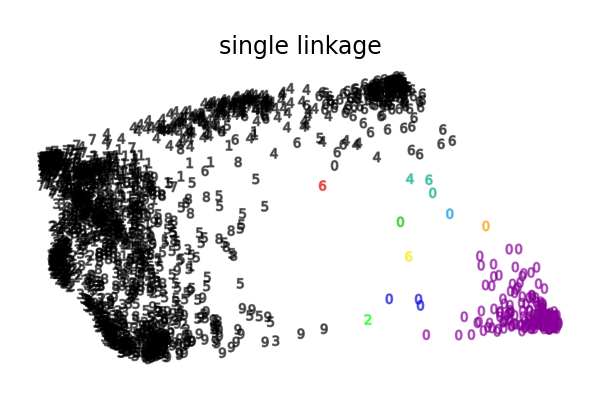
ما يظهره هذا المثال لنا هو سلوك "الأغنياء يزدادون ثراء" للتجميع الهرمي الذي يميل إلى إنشاء أحجام غير متساوية للأقسام.
هذا السلوك ملحوظ لاستراتيجية الربط المتوسطة، التي تنتهي ببضعة أقسام بعدد قليل من النقاط.
حالة الربط الفردي أكثر سوءًا مع قسم كبير يغطي معظم الأرقام، وقسم متوسط الحجم (نظيف) يحتوي على معظم الأصفار وجميع الأقسام الأخرى تتكون من نقاط ضوضاء حول الحواف.
استراتيجيات الربط الأخرى تؤدي إلى أقسام موزعة بشكل متساوٍ أكثر مما يجعلها أقل حساسية لإعادة أخذ عينات عشوائية من مجموعة البيانات.
Computing embedding
Done.
ward : 0.05s
average : 0.08s
complete : 0.05s
single : 0.02s
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
from sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClustering
from time import time
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets, manifold
digits = datasets.load_digits()
X, y = digits.data, digits.target
n_samples, n_features = X.shape
np.random.seed(0)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Visualize the clustering
def plot_clustering(X_red, labels, title=None):
x_min, x_max = np.min(X_red, axis=0), np.max(X_red, axis=0)
X_red = (X_red - x_min) / (x_max - x_min)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
for digit in digits.target_names:
plt.scatter(
*X_red[y == digit].T,
marker=f"${digit}$",
s=50,
c=plt.cm.nipy_spectral(labels[y == digit] / 10),
alpha=0.5,
)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
if title is not None:
plt.title(title, size=17)
plt.axis("off")
plt.tight_layout(rect=[0, 0.03, 1, 0.95])
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
# 2D embedding of the digits dataset
print("Computing embedding")
X_red = manifold.SpectralEmbedding(n_components=2).fit_transform(X)
print("Done.")
for linkage in ("ward", "average", "complete", "single"):
clustering = AgglomerativeClustering(linkage=linkage, n_clusters=10)
t0 = time()
clustering.fit(X_red)
print("%s :\t%.2fs" % (linkage, time() - t0))
plot_clustering(X_red, clustering.labels_, "%s linkage" % linkage)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.715 seconds)
Related examples
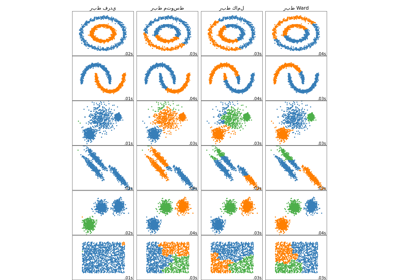
مقارنة طرق الربط الهرمي المختلفة على مجموعات بيانات تجريبية

تعلم متعدد الشعب على الأرقام المكتوبة بخط اليد: التضمين الخطي المحلي، Isomap...